Mapping out the sales process steps is secondary to knowing what a sales process is, when it comes to acquiring, developing and maintaining customers. In the digitally influenced sales process, the goal is no longer so focused so much on giving pitches and pricing, but to offer value propositions personalized to each client. The modern sales process is void of any unnecessary complexity or obstacles in customer interaction.

The term “sales process” usually refers to the series of steps a business has mapped out that gives it the best possible outcome to generate revenue with both new and existing customers. It could form part of the bigger sales playbook. It is different from company to company depending on their industry and complexity or pricing of the product.
In a practical level, the sales process steps act as a prescriptive guide for salespeople to follow when engaging in sales prospecting, business development, retaining customers and closing deals.
Sales Process Steps.
Research shows that the more formal the sales processes steps, the stronger the sales performance.
This is because closing a sale is becoming ever more difficult. Buyers have access to numerous sources of information and can be highly educated when they first come into contact with a salesperson. So, a sales process must plan to intervene with customers further and further upstream in their buyer’s journey.
A modern sales process should be:
- Customer focused
- Clearly outlined
- Prescriptive in nature
- Aligned to buyer’s journey
- Outcome oriented
- Measurable against KPI’s
- Adaptable across channels
Many articles on “what is a sales process” will have the sales process steps starting at Prospecting. However, we see prospecting within the “sales section”, which is the 3rd section of a sales process, with Knowledge and Research being the 1st and 2nd sections respectively.
So, our sales process steps have 3 sections, each section has a series of steps that build to the complete sales process. They are 1. Knowledge Management, 2. Research and 3. Sales.
- Knowledge Management
Knowledgeable management in the sales process steps is about ensuring all salespeople have a thorough understanding of what they are selling and to whom. It includes the sales team being prepared to give in-depth answers to any customer questions, knowledge about their business and industry, sales trends, competition analysis, market trends, how the company’s products solve problems, and where to find resources, information or assets they will use during the sales process.
The knowledge management section in the sales process should also track which questions the sales teams ask the most, what assets and content do they access the most often, and which types of sales touch points or activities that produce the best results.
The inclusion of different customer engagement scenarios, real case studies on how buyers pain points were solved, sales cycle obstacles, how deals were won and how new revenue was generated is also a valuable part of knowledge management.
- Research
Market and sales research, that is having salespeople trained on the target market, ideal customer profiles, target customers, the industry, and the business’s value proposition to the market can never be overstated. Developing a deep understanding of customer profiles., their buying journey and knowing how to acquire sales intelligence is now a key aspect of a sales process. It also includes research on competitors, the core issues buyers usually experience as it relates to the product, and then combine these with market knowledge to understand the key points to address these issues.
Creating a list of “research points” that salespeople must have prior to engaging a prospect or upselling an existing customer should be given strong consideration in the sales process steps.
- Sales
58% of companies don’t have a tailored approach to the different moments in the buyer’s journey.
Now we come to the 3rd section of the sales process. This is the act and activity of engaging with prospects or customers to sell. The challenge for every business is to equip every salesperson with the ability to consistently and systematically have valuable conversations either online or offline with the right set of customers at each stage of the buyer’s journey to optimize the results of the sales process steps.
The guiding principle in any sales process has to be concerned with maximizing selling time, customer acquisition and relationship building.
It needs to be stated that aligning the sales effort with sales process takes work. Sales leaders sometime have to overcome the fear that disrupting the current process will impact revenue. All stakeholders from sales, marketing, support and finance will need to work together to prioritize the expected steps in the sales process. This is about visioning the future, seeing the bigger picture, and focusing on the best sales process steps to boost the time spent selling regardless of past practices.
While the “Sales Section” is the implantation aspect of the sales process, the inclusion of Knowledge Management and Research ensure a more holistic approach to customer engagement. Next, we can take a look at the sales process steps within the sales section.
TYPICAL SALES PROCESS STEPS
Sales Prospecting
This step involves finding and engaging a new set of potential customers using market knowledge and research. Using this information, the salespeople will use a multi-channel approach including social selling, cold calling, cold emails and social networking to engage the prospect. The days of sales Prospecting being a smash and grab event are long gone, it may take weeks or months to build up enough influence with a buyer before a sales conversation can happen. The sales process steps should outline in detail the methodical approach the company wants to undertake for the sales prospecting step in the process.
Nurturing and Collaboration.
This step involves the salesperson nurturing and collaborating with a set of prospects (or existing customers) to understand their business, uncovering needs, gathering information, identifying the buying committee and vitally to ascertain if a need really exists. If a need is found to exist, the salesperson must now get it high enough on the prospects priority list that they will take action. Then they must make buying easy by working with prospect/customer to help them navigate the journey towards making a decision. Again, market knowledge and research play a central role here. This step may be played out over numerous conversations, meetings, free trials, case studies, product demonstrations and proof of concepts prior to moving to the presenting step.
Presenting the Solution
This step (which can be fluid and intermixed when collaborating) is about presenting the proposal or solution. The most successful presenting steps include a buyer urgency lever due to information gathered as the salesperson collaborated with the buyer. The reality is that this step can be time consuming, so it should be positioned deep into the sales process and only reserved for well qualified prospects. This step also handles any objections, hurdles, buying committee concerns or terms. Again, this step will take time, usually with repeated interactions to conclude the deal.
Closing the Sales
This step involves the buyer opting to decide for the salespersons proposal. It entails concluding any final negotiations, terms, pricing, delivery etc. In most sales situations it concludes with a contract or purchase order.
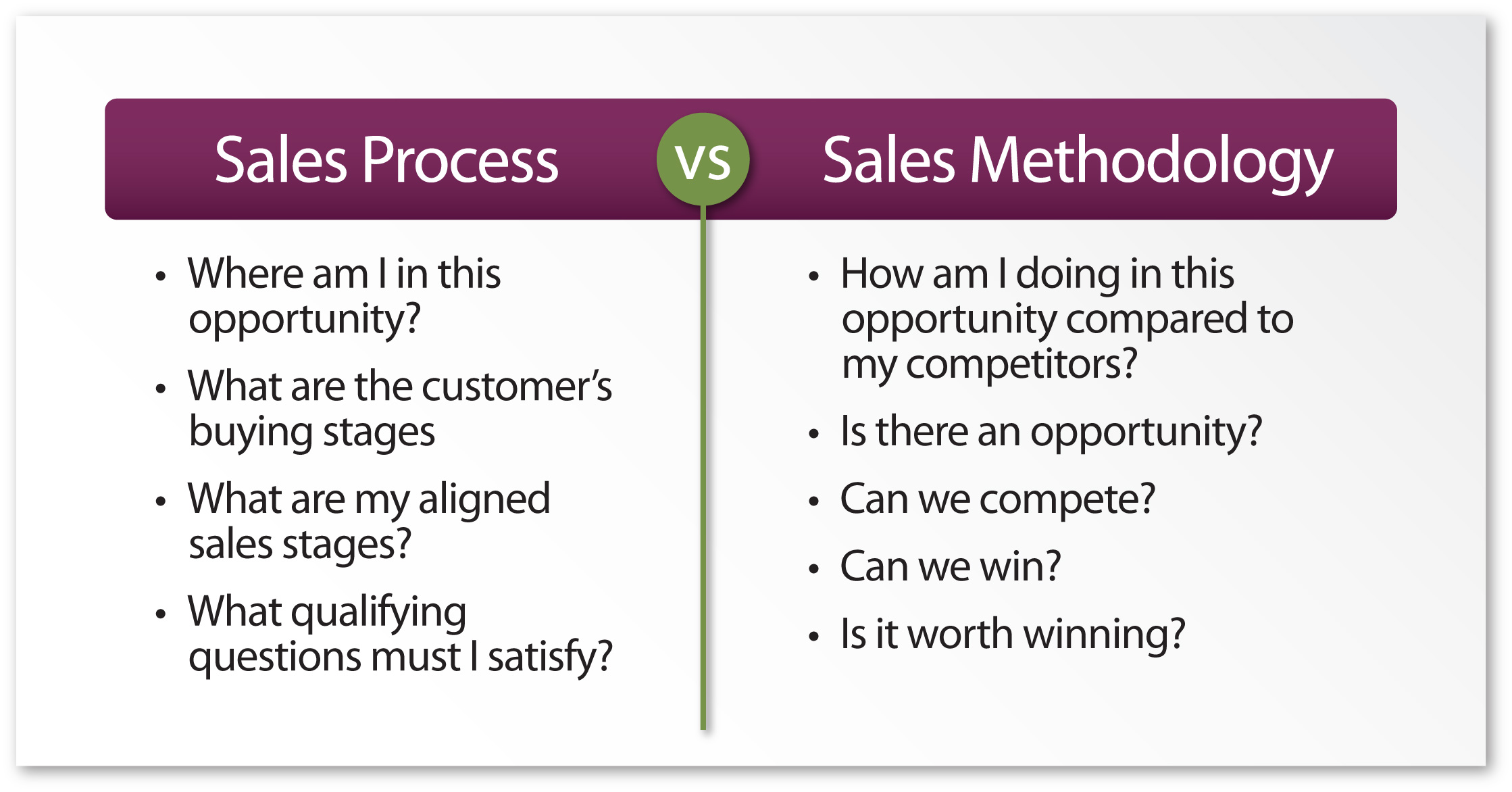
Sales Process is not the same as Sales Methodology
Sales process is different from sales methodology in that the sales process is concerned with “What to do”, that is the specific steps, criteria and list of actions that salespeople must follow in engaging a prospect or client.
Sales methodology is the “How to do it”, the approach, framework and sales techniques given to the salespeople via sales training on how each step in the sales process is expected to be carried out.
Successful companies have both, a strong sales process and a sales team trained on the preferred sales methodology.
Sales is a Process, Not an Event
Implementing sales process steps should result in:
Improved Outcomes. When carried out via a series of set actions, outcomes will improve leading to sales and profits.
Repeatable Activity. All sales activities can be repeated and are repeatable to obtain the same desired outcome by any salesperson time and time again.
Measurable Results. All outcomes can be measured and compared to KPI’s or goals.
Relevant to All. A well mapped out sales process is relevant and understandable to other departments or divisions.
So now you hopefully have at least some insight into the question, what is a sales process? And how to embed all sales activity into the A to Z of the buyer’s journey. Clarity in the sales process gives a business the framework and the time to create a buying vision, the reasons and case why the customer will change (challenge the buyers journey) plus creating the conditions to share insights and information on how the client’s world will change for the better, by choosing you as a partner.